Press
Faulty DNA disposal system causes inflammation
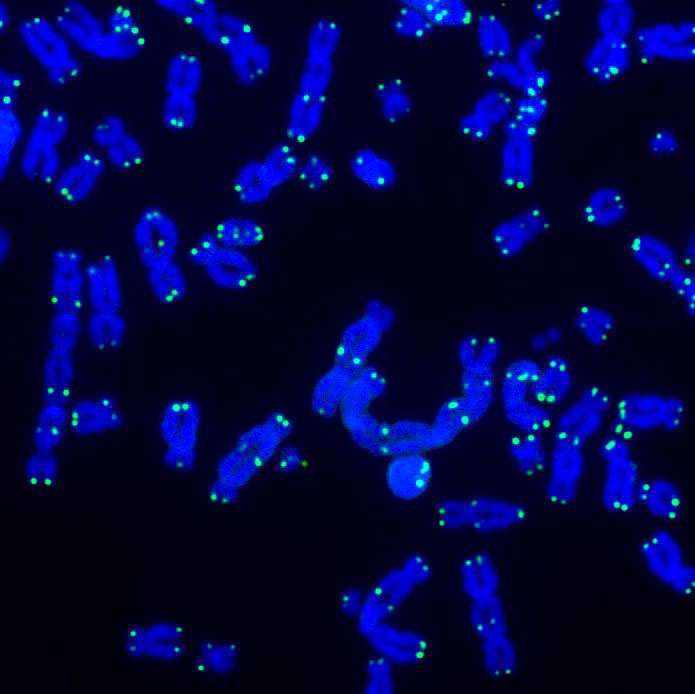
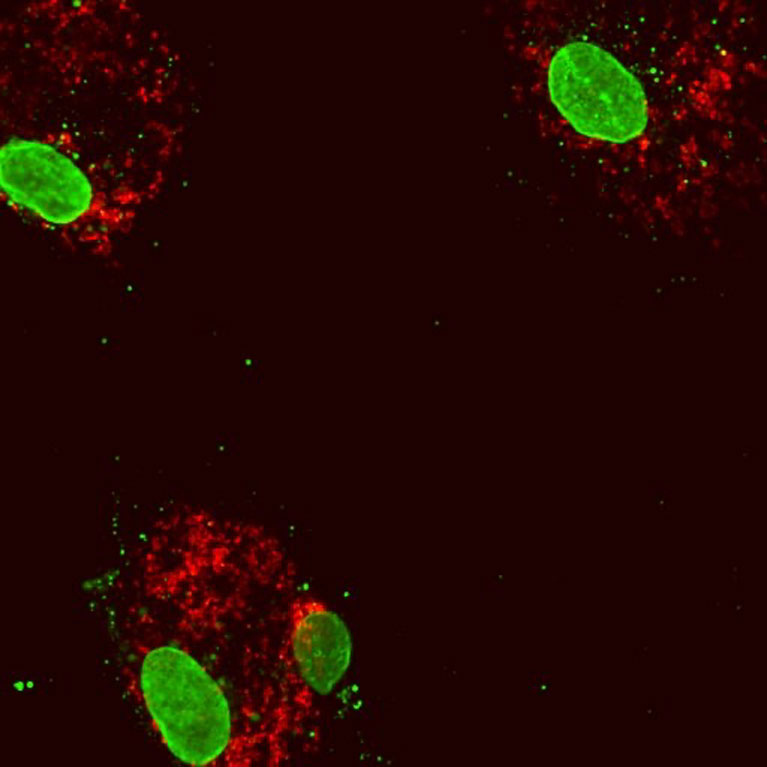
LA JOLLA—Cells in the human body contain power-generating mitochondria, each with their own mtDNA—a unique set of genetic instructions entirely separate from the cell’s nuclear DNA that mitochondria use to create life-giving energy. When mtDNA remains where it belongs (inside of mitochondria), it sustains both mitochondrial and cellular health—but when it goes where it doesn’t belong, it can initiate an immune response that promotes inflammation.
Rewiring tumor mitochondria enhances the immune system’s ability to recognize and fight cancer
LA JOLLA—Immunotherapy, which uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer, is an effective treatment option, yet many patients do not respond to it. Thus, cancer researchers are seeking new ways to optimize immunotherapy so that it is more effective for more people. Now, Salk Institute scientists have found that manipulating an early step in energy production in mitochondria—the cell’s powerhouses—reduces melanoma tumor growth and enhances the immune response in mice.
Telomeres, mitochondria, and inflammation oh my! Three hallmarks of aging work together to prevent cancer
LA JOLLA—As we age, the end caps of our chromosomes, called telomeres, gradually shorten. Now, Salk scientists have discovered that when telomeres become very short, they communicate with mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouses. This communication triggers a complex set of signaling pathways and initiates an inflammatory response that destroys cells that could otherwise become cancerous.
San Diego Nathan Shock Center leverages long-running human study to enable cellular research on diversity of aging
LA JOLLA—The San Diego Nathan Shock Center of Excellence in the Basic Biology of Aging, a collaboration between the Salk Institute, UC San Diego, and Sanford Burnham Prebys, received new funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to enroll participants from the Rancho Bernardo Study of Healthy Aging into their own clinical cohort to study differences in how individuals age. Initiated 50 years ago by the late UC San Diego Distinguished Professor Elizabeth Barrett-Connor, the Rancho Bernardo Study is one of the longest, continuously NIH-funded studies in existence.
Scientists find surprising link between mitochondrial DNA and increased atherosclerosis risk
LA JOLLA— Mitochondria are known as cells’ powerhouses, but mounting evidence suggests they also play a role in inflammation. Scientists from the Salk Institute and UC San Diego published new findings in Immunity on August 2, 2022, where they examined human blood cells and discovered a surprising link between mitochondria, inflammation and DNMT3A and TET2—two genes that normally help regulate blood cell growth but, when mutated, are associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
San Diego Nathan Shock Center announces pilot grant awardees
LA JOLLA—The San Diego Nathan Shock Center (SD-NSC) of Excellence in the Basic Biology of Aging, a consortium between the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, Sanford Burnham Prebys (SBP) and the University of California San Diego, has announced its second-year class of pilot grant awardees. Recipients from six different institutions will receive up to $15,000 to pursue research that advances our understanding of how humans age, with the ultimate goal of extending health span, the number of years of healthy, disease-free life.
Peter Adams and Gerald Shadel awarded $13 million from NIH to study aging and liver cancer
LA JOLLA—Sanford Burnham Prebys Professor Peter D. Adams, who directs the Aging, Cancer and Immuno-oncology Program, and Salk Institute Professor Gerald Shadel, who directs the San Diego Nathan Shock Center of Excellence in the Basic Biology of Aging, have been awarded a grant from the NIH’s National Institute on Aging for $13 million, funding a five-year project to explore the connection between aging and liver cancer.
Top San Diego research institutions, led by Salk, to receive an expected $5 million to study cellular aging in humans
LA JOLLA—The Salk Institute will establish a world-class San Diego Nathan Shock Center (SD-NSC), a consortium with Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute and the University of California San Diego (UC San Diego), to study cellular and tissue aging in humans. The Center will be funded by a grant from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) of the National Institutes of Health expected to total $5 million over the next 5 years (NIA grant number P30AG068635).
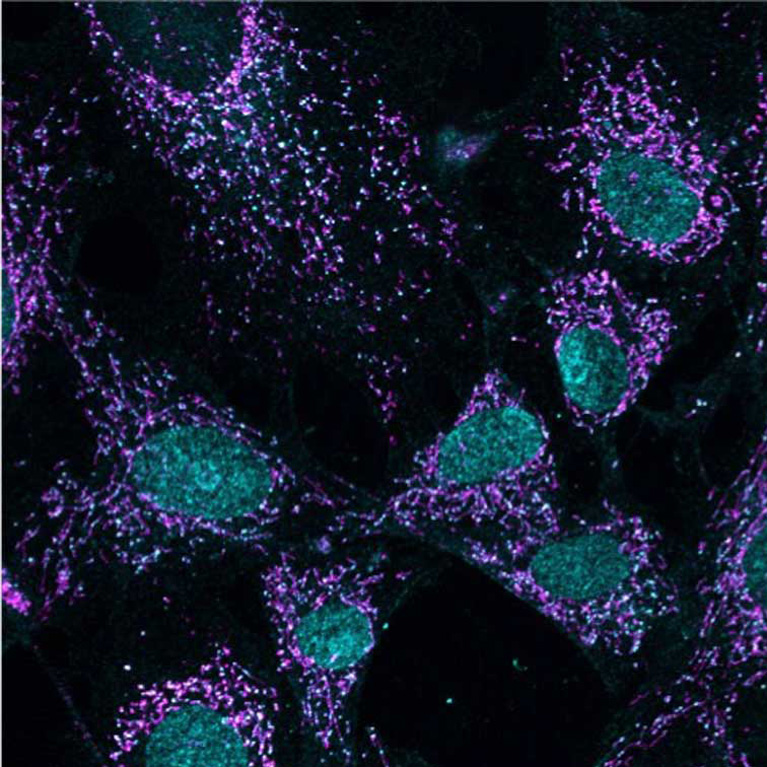
Mitochondria are the “canary in the coal mine” for cellular stress
LA JOLLA—Mitochondria, tiny structures present in most cells, are known for their energy-generating machinery. Now, Salk researchers have discovered a new function of mitochondria: they set off molecular alarms when cells are exposed to stress or chemicals that can damage DNA, such as chemotherapy. The results, published online in Nature Metabolism on December 9, 2019, could lead to new cancer treatments that prevent tumors from becoming resistant to chemotherapy.
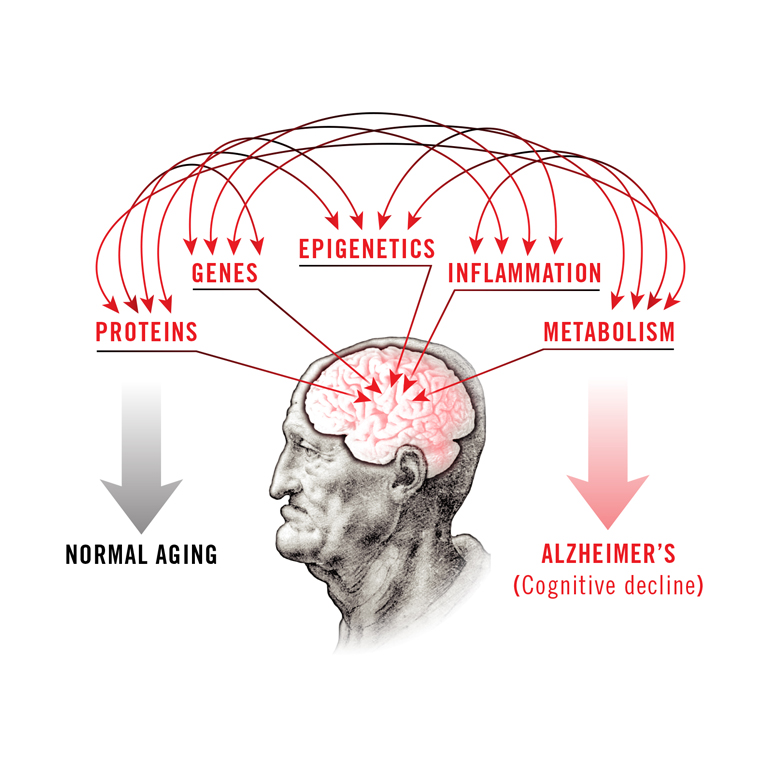
Salk awarded $19.2 million by the American Heart Association-Allen Initiative to study Alzheimer’s and aging in the brain
LA JOLLA—A team of Salk Institute researchers led by President Rusty Gage has been awarded $19.2 million over eight years by the American Heart Association-Allen Initiative in Brain Health and Cognitive Impairment to investigate mechanisms underlying Alzheimer’s disease and aging-related cognitive decline and uncover new therapies. This bold venture will comprehensively analyze interactions between five areas key to brain health: proteins, genes, metabolism, inflammation and epigenetics.
Cells agree: what doesn’t kill you makes you stronger
LA JOLLA—We’ve all heard the expression: “what doesn’t kill you makes you stronger.” Now, research led by a Salk Institute scientist suggests why, at a cellular level, this might be true. The team reports that brief exposures to stressors can be beneficial by prompting the cell to trigger sustained production of antioxidants, molecules that help get rid of toxic cellular buildup related to normal metabolism.
An ATM that dispenses antioxidants
LA JOLLA—One reason we’re supposed to eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables is because they contain nutritious compounds called antioxidants. These molecules counteract the damage to our bodies from harmful products of normal cells called reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Three Salk faculty honored with endowed chairs
LA JOLLA—Salk scientists Katherine Jones, Susan Kaech and Gerald Shadel each have been recognized for their contributions and dedication to advancing science through research by being named to endowed chairs at the Institute.
Prominent scientists in immunobiology and aging research to join Salk Institute
LA JOLLA—The Salk Institute is honored to welcome two new faculty with the rank of full professor, both of whom are highly respected and accomplished leaders in their fields. Susan Kaech and Gerald Shadel will inspire fresh collaborations and bring experienced perspectives to bear on Salk’s approaches to health and disease.